AEROSOL-TLN - Monitoring atmospheric deposits in Toulon harbour
Station managers : Gaël Durrieu & Benjamin Oursel
Partner : IFREMER la Seyne sur Mer
Context
The Toulon roadstead, located in the north-western Mediterranean Sea, is a semi-enclosed bay of around 52 km², divided into 2 unequal sections (Petite and Grande Rade) by an artificial dyke. It is subject to a weak tidal current, intermittent and relatively small freshwater inflows (from the Las and Eygoutier catchment areas) and the influence of a conurbation with a population of around 0.5 million, as well as various human activities (national navy, 1.3 million passengers/year by ferry, aquaculture, tourism, etc.).
The particularity of the site studied also lies in the strong effects of the prevailing winds (mistral and easterly) on the distribution of contaminated fine particles and their deposits. Historically, the Rade de Toulon has long been an important port and is currently France's leading military port.
Given its characteristics, the Rade de Toulon has been a workshop site for M.I.O. for a number of years. A great deal of scientific work has been published on this system (Tessier et al., 2011; Dang et al., 2014 and 2015; Coclet et al., 2018 and 2020; Layglon et al., 2020), helping managers and decision-makers to identify chemical contamination, trace its sources and assess its real impact on living organisms.
Description and objectives
In 2019, as part of G. Durrieu's thesis, the M.I.O. CEM team decided to install a dry and wet deposition sampler (on loan from IRB-Croatia) on the roof of an IFREMER building located in the Brégaillon port area at La Seyne sur Mer (figure 1, 43°06'25.1″N 5°53'04.6″E). The aim of this study is to precisely characterise the chemical quality of aerosols deposited in this anthropised ecosystem that is the Rade de Toulon. The ultimate objective is to determine the contribution of aerosols to the flow of contaminants into the harbour. Monthly monitoring has been carried out since July 2019 for dry deposits and after each rainfall for wet deposits. The treatments and analyses carried out on these deposits are detailed in figure 2. A meteorological station is also installed on the site, providing information on wind direction and speed, temperature, humidity levels, etc.
In 2022, to follow up the results of G. Durrieu's thesis, the CEM team decided to continue this observation station and to continue taking samples. At the beginning of 2023, a sampler of the same type as that used in IR-ILICO's MOOSE observation network was purchased with the team's own funds (Figure 1), so that our study could be compared with the MOOSE data.
A database is thus created. The data can be retrieved, subject to conditions, by e-mail from G. Durrieu and B. Oursel.
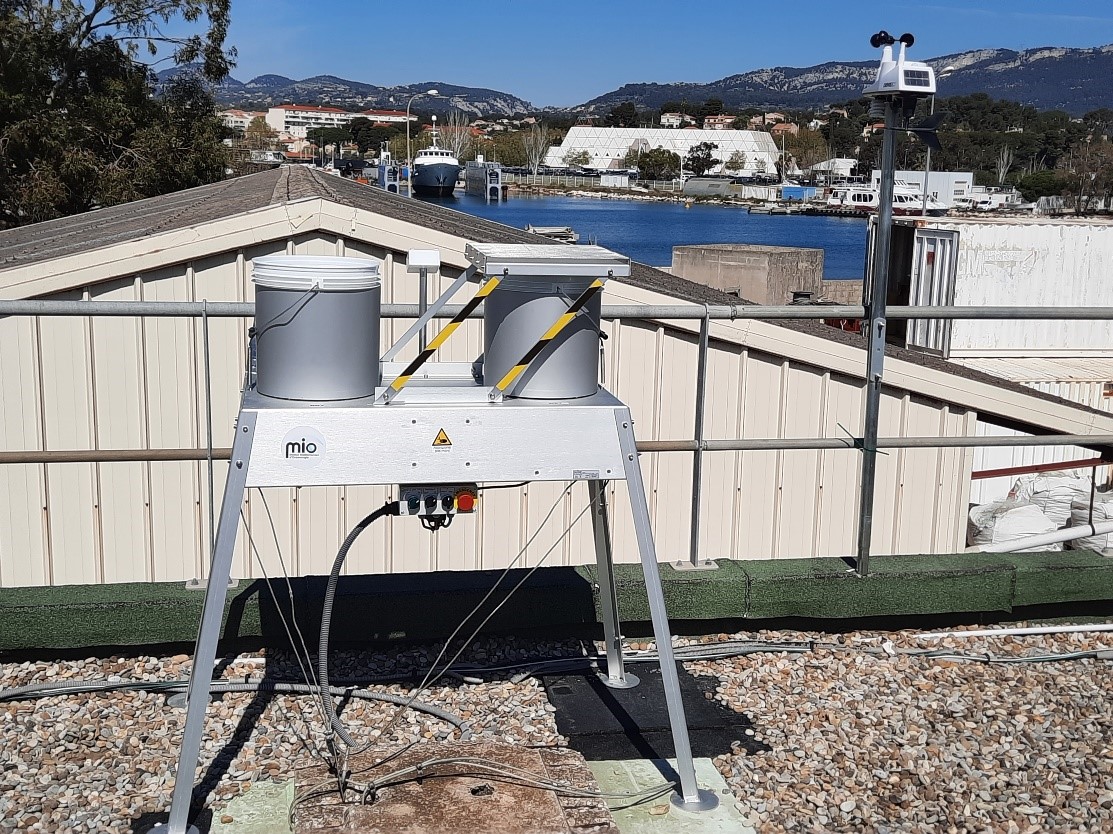

Figure 1: Photograph of the atmospheric deposition sampler and the weather station
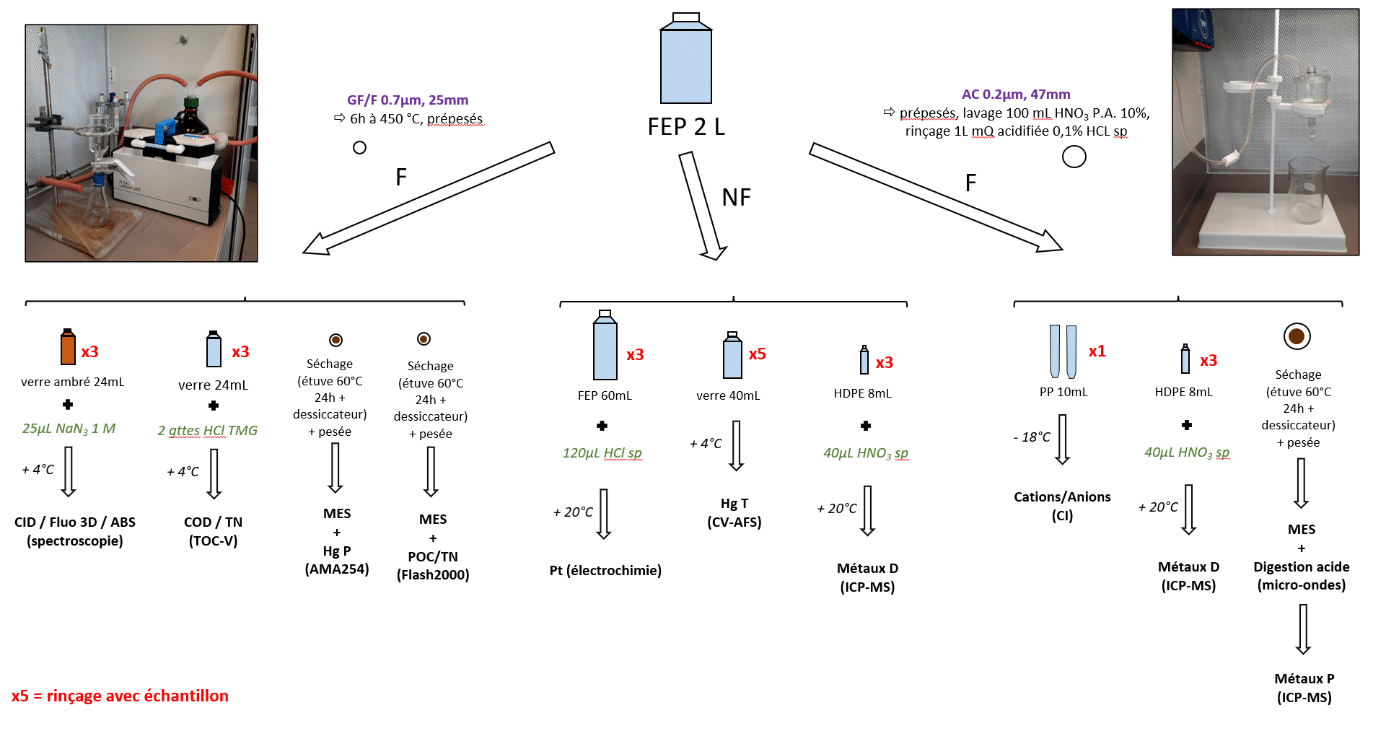
Figure 2: Descriptive diagram of the treatments and analyses carried out on the deposits
References
Coclet C., Garnier C., Delpy F., Jamet D., Gurrieu G., Le Poupon C., Mayer M. & B. Misson, 2018, Tarce metal contamination as a toxic and structuring factor impacting ultraphytoplankton communities in a multicontaminated Mediterranean coastal areaProgess in Oceanography, DOI: 10.1016/j.pocean.2017.06.006.
Coclet C., Garnier C., Durrieu G., D'Onofrio S., Layglon N., Briand J-F. & Misson B., 2020, Impacts of copper and lead exposure on prokaryotic communities from contaminated contrasted coastal seawaters: the influence of previous metal exposure, FEMS Microbiology Ecology, DOI: 10.1093/femsec/fiaa048.
Dang D.H., Tessier E., Lenoble V., Durrieu G., Omanovic D., Mullot J-U., Pfeifer H-R., Mounier S. & Garnier C., 2014, Key parameters controlling arsenic dynamics in coastal sediments: An analytical and modelling approach, Marine Chemistry, DOI: 10.1016/j.marchem.2014.02.005.
Dang D.H., Schäfer J., Brach-Papa C., Lenoble V., Durrieu G., Dutruch L., Chiffoleau J-F., Gonzales J-L., Blanc G., Mullot J-U., Mounier S. & Garnier C., 2015, Evidencing the impact of coastal contaminated sediments on mussels through Pb stable isotopes composition, Environmental Science and Technology, DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.5b01893.
Layglon N., Misson M., Durrieu G., Coclet C., D'Onofrio S., Dang D.H., François D., Mullot J-U., Mounier S., Lenoble V., Omanovic D. & Garnier C., 2020, Long-term monitoring emphasises the impacts of the dredging on dissolved Cu and Pb contamination along with ultraplankton distribution and structure in Toulon Bay (NW Mediterranean Sea, France), Marine Pollution Bulletin, DOI: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111196.
Tessier E., Garnier C., Mullot J-U., Lenoble V., Arnaud M., Raynaud M. & Mounier S., 2011, Study of the spatial and historical distribution of sediment inorganic contamination in the Toulon Bay (France), Marine Pollution Bulletin, DOI: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.07.022.




